Patient counselling information
What is Empagliflozin and for which conditions it is used?
Empagliflozin is a medicine belongs to class sodium glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors and used for management of diabetes, heart failure, chronic kidney diseases.
What you need to know before you take Empagliflozin? What are warnings and precautions to consider while using Empagliflozin?
Do not take Empagliflozin, if you are allergic to empagliflozin or any of the other ingredients of this medicine
Warnings and precautions: Contact a doctor or the nearest hospital straight away:
Ketoacidosis: If you experience rapid weight loss, feeling sick or being sick, stomach pain, excessive thirst, fast and deep breathing, confusion, unusual sleepiness or tiredness, a sweet smell to your breath, a sweet or metallic taste in your mouth, or a different odour to your urine or sweat, contact a doctor or the nearest hospital straight away.
Talk to your doctor, pharmacist before taking this medicine, and during treatment:
- If you have serious kidney problems
- If you have serious liver problems
- If you are taking medicines that increase urine production [diuretics] or lower blood pressure
- If you are 75 years old or older.
- If you have a serious infection of the kidney or the urinary tract with fever
Talk to your doctor immediately if you develop a combination of symptoms of pain, tenderness, redness, or swelling of the genitals or the area between the genitals and the anus with fever or feeling generally unwell. These symptoms could be a sign of a rare but serious or even life-threatening infection, called necrotising fasciitis of the perineum or Fournier´s gangrene which destroys the tissue under the skin. Fournier’s gangrene has to be treated immediately.
Can Empagliflozin be used in Children and adolescents?
Empagliflozin can be used in children aged 10 years and older for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. No data are available in children below 10 years of age. Empagliflozin is not recommended for children and adolescents under 18 years of age for the treatment of heart failure or for the treatment of chronic kidney disease, because it has not been studied in these patients.
Can Empagliflozin be used during Pregnancy and breast-feeding?
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking this medicine. Do not use Empagliflozin if you are pregnant. It is unknown if Empagliflozin is harmful to the unborn child. Do not use Empagliflozin if you are breast-feeding. It is not known if Empagliflozin passes into human breast milk.
What is the dose of Empagliflozin?
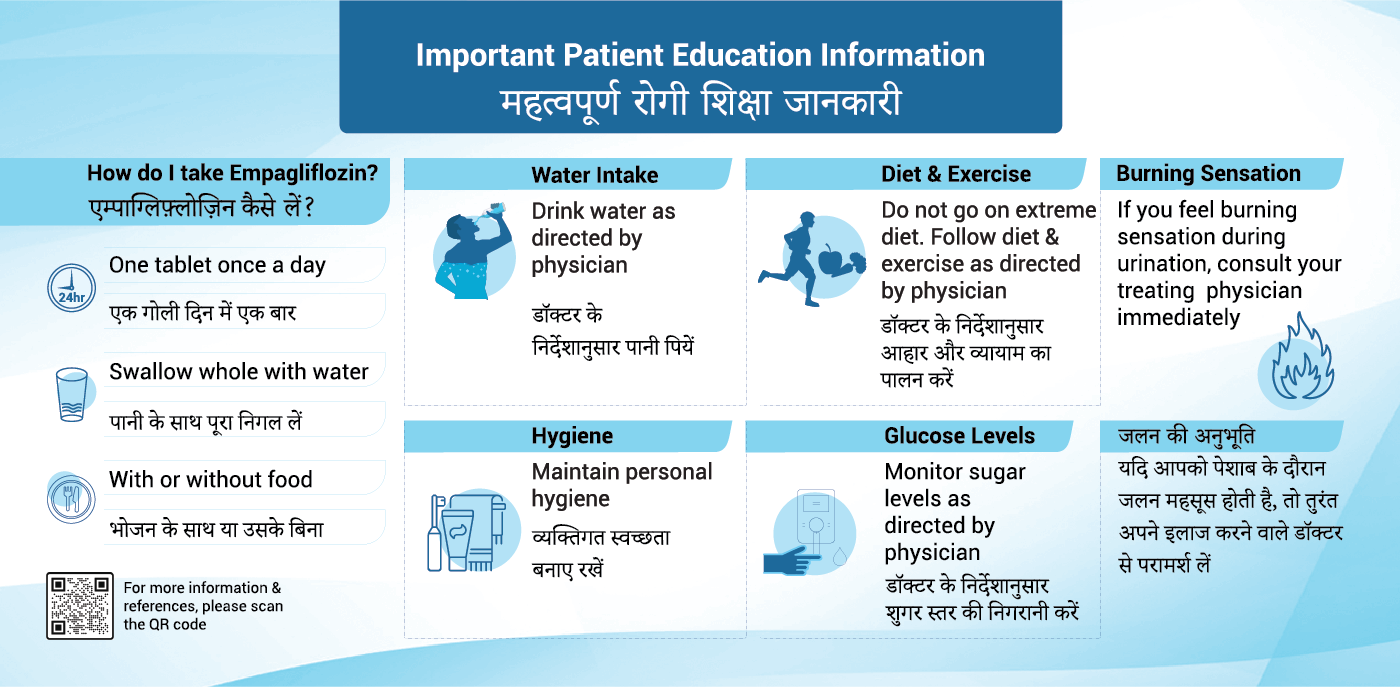
The recommended dose of Empagliflozin is one 10 mg tablet once a day. If you have type 2 diabetes mellitus, your doctor will decide whether to increase your dose to 25 mg once a day, if needed to help to control your blood sugar. Your doctor may limit your dose to 10 mg once a day if you have a kidney problem.
Your doctor will prescribe the strength that is right for you. Do not change your dose unless your doctor has told you to.
How to take empagliflozin?
- Swallow the tablet whole with water
- You can take the tablet with or without food
- You can take the tablet at any time of the day. However, try to take it at the same time each day. This will help you to remember to take it.
- If you have type 2 diabetes mellitus, your doctor may prescribe Empagliflozin together with another diabetes medicine. Remember to take all medicines as directed by your doctor to achieve the best results for your health.
- Appropriate diet and exercise help your body use its blood sugar better. It is important to stay on the diet and exercise program recommended by your doctor while taking Empagliflozin.
What if you forget to take Empagliflozin?
What to do if you forget to take a tablet depends on how long it is until your next dose.
If it is 12 hours or more until your next dose, take Empagliflozin as soon as you remember. Then take your next dose at the usual time.
If it is less than 12 hours until your next dose, skip the missed dose. Then take your next dose at the usual time.
Do not take a double dose of Empagliflozin to make up for a forgotten dose.
What If you stop taking Empagliflozin?
Do not stop taking Empagliflozin without first consulting your doctor, unless you suspect you have ketoacidosis (see “ketoacidosis” under “warnings and precautions”). If you have type 2 diabetes mellitus, your blood sugar levels may increase when you stop taking Empagliflozin.
What are the possible side effects of Empagliflozin?
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them. Contact a doctor or the nearest hospital straight away if you have any of the following side effects:
- Severe allergic reaction, seen uncommonly (may affect up to 1 in 100 people) : Possible signs of severe allergic reaction may include: swelling of the face, lips, mouth, tongue, or throat that may lead to difficulty breathing or swallowing)
- Ketoacidosis, seen uncommonly (may affect up to 1 in 100 people): rapid weight loss, feeling sick or being sick, stomach pain, excessive thirst, fast and deep breathing, confusion, unusual sleepiness or tiredness, a sweet smell to your breath, a sweet or metallic taste in your mouth or a different odour to your urine or sweat.
- Low blood sugar (hypoglycaemia), seen very commonly (may affect more than 1 in 10 people): If you take Empagliflozin with another medicine that can cause low blood sugar, such as a sulphonylurea or insulin, your risk of getting low blood sugar is higher. The signs of low blood sugar may include: shaking, sweating, feeling very anxious or confused, fast heart beat, excessive hunger, headache
- Urinary tract infection, seen commonly (may affect up to 1 in 10 people): The signs of urinary tract infection are: burning sensation when passing urine, urine that appears cloudy, pain in the pelvis, or mid-back pain (when kidneys are infected). An urge to pass urine or more frequent urination may be due to the way Empagliflozin works, but they can also be signs of urinary tract infection. If you note an increase in such symptoms, you should also contact your doctor.
- Dehydration, seen very commonly (may affect more than 1 in 10 people): The signs of dehydration are not specific, but may include: unusual thirst, lightheadedness or dizziness upon standing, fainting or loss of consciousness
Are there any foods, drinks, or activities I should avoid?
Limit alcohol, as it may increase the risk of low blood sugar, especially if you’re also on insulin or other diabetes medications. Reducing high-sugar foods can help manage blood sugar more effectively.
What precautions should I take if I have kidney disease?
Empagliflozin is not recommended for people with severe kidney impairment (eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m²). If you have kidney disease, your healthcare provider will evaluate your condition to determine if empagliflozin is suitable for you
How will I know if I have a urinary or genital infection, and what should I do?
Symptoms of infection may include painful urination, itching, or unusual discharge. Contact your doctor if you notice any of these signs for prompt treatment
What medications might interact with empagliflozin?
Diuretics, insulin, and sulfonylureas can increase dehydration or hypoglycemia risks when taken with empagliflozin. Inform your doctor of all medications and supplements to avoid potential interactions
Can empagliflozin cause low blood pressure, especially for older adults?
Yes, particularly in elderly patients or those on diuretics. Watch for symptoms like dizziness or fainting. Staying hydrated can help manage blood pressure while on empagliflozin
Does empagliflozin cause weight loss, and should I monitor my weight?
Some people may experience mild weight loss as empagliflozin helps remove excess glucose. Monitoring your weight can help track any unintended changes
Should I stop empagliflozin before surgery or a medical procedure?
It’s important to consult your doctor, as empagliflozin may need to be paused before surgery to reduce the risk of DKA. Follow their instructions closely
Can I use empagliflozin if I have type 1 diabetes?
Empagliflozin is not approved for type 1 diabetes due to a higher risk of diabetic ketoacidosis. It’s only indicated for type 2 diabetes management
How often will my blood glucose and HbA1c levels need to be checked?
Your doctor may check your HbA1c every 3 to 6 months to monitor long-term glucose control. Regular self-monitoring of blood glucose may also be needed, especially if you’re adjusting doses

References
- Prescribing information Empagliflozin. Available from https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/204629s033lbl.pdf. Cited on 14 Oct 2024
- Summary of Product characteristics. Available from https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/Empagliflozin-epar-product-information_en.pdf Cited on 14 Oct 2024
- Empagliflozin NHS. Available from https://www.nhs.uk/medicines/empagliflozin/ cited on 14 Oct 2024