Patient counselling information
What is Empagliflozin– Sitagliptin fixed dose combination and for which conditions it is used?
It is a prescription medicine that contains 2 diabetes medicines, empagliflozin and Sitagliptin. It can be used along with diet and exercise to lower blood sugar in adults with type 2 diabetes, in adults with type 2 diabetes who have known cardiovascular disease when empagliflozin, one of the medicines in this FDC, is needed to reduce the risk of cardiovascular death.
What you need to know before you take Empagliflozin-Sitagliptin? What are warnings and precautions to consider while using it?
Do not take Empagliflozin-sitagliptin- if you are allergic to empagliflozin, sitagliptin, any other SGLT2 inhibitor (e.g. dapagliflozin, canagliflozin), any other DPP-4 inhibitor (e.g. Linagliptin, vildagliptin), or any of the other ingredients of this medicine.
Warnings and precautions
Talk to your doctor, before taking this medicine, and during treatment:
- if you have “type 1 diabetes”. This type usually starts when you are young and your body does not produce any insulin. You should not take Empagliflozin-sitagliptin if you have type 1 diabetes.
- if you experience rapid weight loss, feeling sick or being sick, stomach pain, excessive thirst, fast and deep breathing, confusion, unusual sleepiness or tiredness, a sweet smell to your breath, a sweet or metallic taste in your mouth, or a different odour to your urine or sweat, contact a doctor or the nearest hospital straight away and stop taking this medicine until further advice from your doctor. These symptoms could be a sign of “diabetic ketoacidosis” – a rare, but serious, sometimes life-threatening problem you can get with diabetes because of increased levels of “ketone bodies” in your urine or blood, seen in tests. The risk of developing diabetic ketoacidosis may be increased with prolonged fasting, excessive alcohol consumption, dehydration or sudden reductions in insulin dose, or a higher need of insulin due to major surgery or serious illness.
- if you are taking other anti-diabetic medicines known as “sulphonylurea” (e.g. glimepiride, glipizide) and/or using insulin. Your doctor may want to reduce your dose of these medicines when you take them together with Empagliflozin- Sitagliptin, in order to avoid too low blood sugar (hypoglycemia).
- if you have or have had a disease of the pancreas.
- if you have serious kidney problems. Your doctor may limit your daily dose or ask you to take a different medicine
- if you have serious liver problems. Your doctor may ask you to take a different medicine.
-
if you might be at risk of dehydration, for example:
- if you are being sick, have diarrhea or fever, or if you are not able to eat or drink
- if you are taking medicines that increase urine production [diuretics] or lower blood pressure
- if you are over 75 years old
- Your doctor may ask you to stop taking Empagliflozin-sitagliptin until you recover to prevent loss of too much body fluid. Ask about ways to prevent dehydration.
- if you have an increase in the proportion of red blood cells in your blood (haematocrit), seen in laboratory blood tests.
Contact your doctor if you experience any of the following during treatment with Empagliflozin- Sitagliptin:
- if you develop symptoms of acute pancreatitis, like persistent, severe stomach ache (abdominal pain). Possible signs are listed in section, ‘Possible side effects’. Your doctor may need to change your treatment.
- if you have a serious infection of the kidney or the urinary tract with fever. Your doctor may ask you to stop taking Empagliflozin-sitagliptin until you have recovered.
- if you encounter blistering of the skin it may be a sign for a condition called bullous pemphigoid. Your doctor may ask you to stop Empagliflozin- Sitagliptin.
Talk to your doctor immediately if you develop a combination of symptoms of pain, tenderness, redness, or swelling of the genitals or the area between the genitals and the anus with fever or feeling generally unwell. These symptoms could be a sign of a rare but serious or even life-threatening infection, called necrotizing fasciitis of the perineum or Fournier´s gangrene which destroys the tissue under the skin. Fournier’s gangrene has to be treated immediately.
Foot care: Like for all diabetic patients it is important to check your feet regularly and adhere to any other advice regarding foot care given by your health care professional.
Kidney function: Before you start treatment with Empagliflozin-sitagliptin and regularly during treatment, your doctor will check how well your kidneys are working.
Urine glucose: Because of how this medicine works, your urine will test positive for sugar while you are taking this medicine.
Children and adolescents This medicine is not recommended for children and adolescents under 18 years as sitagliptin is not effective in children and adolescents between the ages of 10 and 17 years. It is not known if this medicine is safe and effective when used in children younger than 10 years
Can Empagliflozin be used during Pregnancy and breast-feeding?
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking this medicine. Do not use Empagliflozin-sitagliptin if you are pregnant. It is unknown if Empagliflozin-sitagliptin is harmful to the unborn child. Do not use Empagliflozin-sitagliptin if you are breast-feeding. It is not known if Empagliflozin/Sitagliptin passes into human breast milk.
What is the dose of Empagliflozin-Sitagliptin?
The usual starting dose is one film-coated tablet of Empagliflozin-sitagliptin10 mg/100 mg once a day. Your doctor will decide whether you need to increase your dose to one film-coated tablet of Empagliflozin-sitagliptin 25 mg/100 once a day. If you already take 25 mg empagliflozin and 100 sitagliptin as separate tablets and you switch to the FDC, you can start directly with Empagliflozin-sitagliptin 25 mg/100 mg.
Renal impairment
Talk to your doctor if you have kidney problems. Your doctor may limit your dose or decide to use an alternative medicine. Hepatic impairment Talk to your doctor in case you suffer from severe hepatic impairment. Empagliflozin-sitagliptin is not recommended and your doctor may decide to use an alternative medicine.
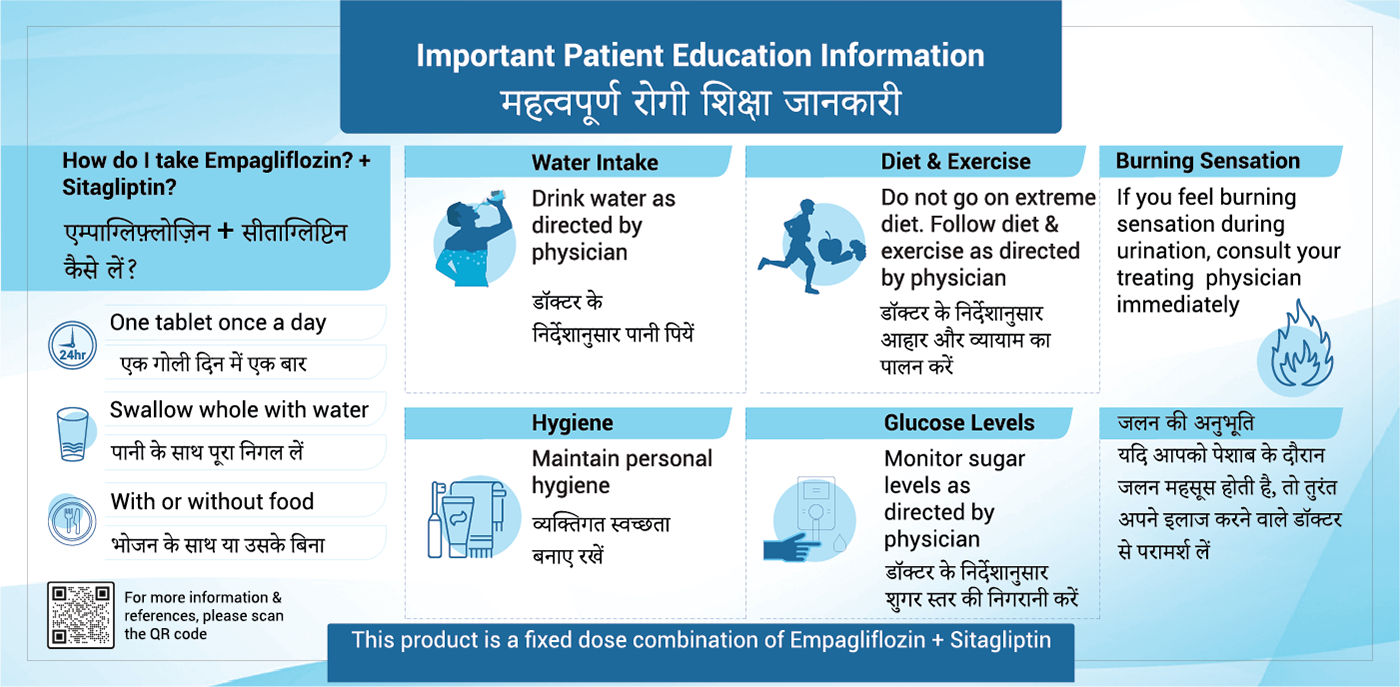
How to take EMPAGLIFLOZIN-SITAGLIPTIN FDC?
Take EMPAGLIFLOZIN-SITAGLIPTIN exactly as your doctor tells you to take it.
- Take FDC one time each day in the morning, with or without food.
- If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If you do not remember until it is time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and go back to your regular schedule. Do not take two doses of FDC at the same time.
- Your doctor may tell you to take FDC along with other diabetes medicines. Low blood sugar can happen more often when FDC is taken with certain other diabetes medicines.
- If you take too much FDC, call your doctor or local poison control center or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
- When your body is under some types of stress, such as fever, trauma (such as a car accident), infection, or surgery, the amount of diabetes medicine that you need may change. Tell your doctor right away if you have any of these conditions and follow your doctor’s instructions.
- Check your blood sugar as your doctor tells you to.
- Stay on your prescribed diet and exercise program while taking the FDC
- Talk to your doctor about how to prevent, recognize and manage low blood sugar (hypoglycemia), high blood sugar (hyperglycemia), and complications of diabetes.
- Your doctor will check your diabetes with regular blood tests, including your blood sugar levels and your hemoglobin A1C.
- When taking FDC, you may have sugar in your urine, which will show up on a urine test.
What if you forget to take Empagliflozin- Sitagliptin?
What to do if you forget to take a tablet depends on how long it is until your next dose.
If it is 12 hours or more until your next dose, take Empagliflozin-sitagliptin as soon as you remember. Then take your next dose at the usual time.
If it is less than 12 hours until your next dose, skip the missed dose. Then take your next dose at the usual time.
Do not take a double dose of Empagliflozin-sitagliptin to make up for a forgotten dose.
What If you stop taking Empagliflozin- Sitagliptin?
Do not stop taking Empagliflozin-sitagliptin without first consulting your doctor, unless you suspect you have ketoacidosis. If you have type 2 diabetes mellitus, your blood sugar levels may increase when you stop taking Empagliflozin- Sitagliptin.
What are the possible side effects of Empagliflozin/Sitagliptin?
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Contact a doctor or the nearest hospital straight away if you have any of the following side effects:
Diabetic ketoacidosis, seen rarely (may affect up to 1 in 1 000 people)
These are the signs of diabetic ketoacidosis (see also section 2, ‘Warnings and precautions’):
- increased levels of “ketone bodies” in your urine or blood
- rapid weight loss
- feeling sick or being sick
- stomach pain
- excessive thirst
- fast and deep breathing
- confusion
- unusual sleepiness or tiredness
- a sweet smell to your breath, a sweet or metallic taste in your mouth or a different odour to your urine or sweat.
This may occur regardless of blood glucose level. Your doctor may decide to temporarily or permanently stop your treatment with this medicine.
Contact your doctor immediately if you notice any of the following side effects:
Allergic reactions, seen uncommonly (may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
This medicine may cause allergic reactions, which may be serious, including hives (urticaria) and swelling of the face, lips, tongue, and throat that may cause difficulty in breathing or swallowing (angioedema).
Inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis), seen uncommonly
This medicine may cause pancreatitis, which usually shows as persistent, severe abdominal (stomach) pain that might reach through to your back, often accompanied by feeling sick or being sick. Your doctor will need to change your treatment.
Low blood sugar (hypoglycaemia), seen commonly (may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
If you take Empagliflozin-sitagliptin with another medicine that can cause low blood sugar, such as a sulphonylurea or insulin, you are at risk of getting too low blood sugar (hypoglycaemia). The signs of too low blood sugar may include:
- shaking, sweating, feeling very anxious or confused, fast heart beat
- excessive hunger, headache
Your doctor will tell you how to treat low blood sugar levels and what to do if you get any of the signs above. If you have symptoms of low blood sugar, eat glucose tablets, a high sugar snack or drink fruit juice. Measure your blood sugar if possible and rest.
Urinary tract infection, seen commonly
The signs of urinary tract infection are:
- burning sensation when passing urine
- urine that appears cloudy
- pain in the pelvis, or mid-back pain (when kidneys are infected)
An urge to pass urine or more frequent urination may be due to the way this medicine works, but as they can also be signs of urinary tract infection, if you note an increase in such symptoms, you should also contact your doctor.
Loss of body fluid (dehydration), seen uncommonly
The signs of dehydration are not specific, but may include:
- unusual thirst
- lightheadedness or dizziness upon standing
- fainting or loss of consciousness
Other side effects while taking Empagliflozin- Sitagliptin:
Seen commonly
- genital yeast infection like thrush
- inflamed nose or throat (nasopharyngitis)
- cough
- passing more urine than usual or needing to pass urine more often
- itching
- skin rash
- increased blood enzyme amylase
- increased pancreas enzyme lipase
- thirst
- constipation
Seen uncommonly
- straining or pain when emptying the bladder
- laboratory blood tests may show changes in blood fat levels, an increase in the amount of red blood cells (increase in haematocrit), and changes related to kidney function (decrease in filtration rate and increase in blood creatinine)
Seen rarely
- sore in the mouth
- necrotising fasciitis of the perineum or Fournier´s gangrene, a serious soft tissue infection of the genitals or the area between the genitals and the anus
Seen very rarely
- inflammation of the kidneys (tubulointerstitial nephritis)
- Frequency not known (cannot be estimated from the available data)
- blistering of skin (bullous pemphigoid)
What precautions should I take if I have kidney disease?
If you have kidney disease, your healthcare provider will evaluate your condition to determine if empagliflozin/Sitagliptin is suitable for you.
How will I know if I have a urinary or genital infection, and what should I do?
Symptoms of infection may include painful urination, itching, or unusual discharge. Contact your doctor if you notice any of these signs for prompt treatment.
What medications might interact with empagliflozin/Sitagliptin?
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using, have recently used or might use any other medicines. In particular, you should tell your doctor if you are using the following medicines:
- Other anti-diabetic medicines, such as insulin or a sulphonylurea. Your doctor may want to lower the dose of these other medicines, to prevent your blood sugar levels from getting too low.
- Medicines used to remove water from your body (diuretics). Your doctor may ask you to stop taking Empagliflozin- Sitagliptin.
- Medicines that might have an effect on the break down of empagliflozin or sitagliptin in your body such as rifampicin (an antibiotic used to treat tuberculosis) or certain medicines used to treat seizures (such as carbamazepine, phenobarbital or phenytoin). The effect of Empagliflozin-sitagliptinmay be reduced.
- Lithium because Empagliflozin-sitagliptincan lower the amount of lithium in your blood.
Can empagliflozin cause low blood pressure, especially for older adults?
Yes, particularly in elderly patients or those on diuretics. Watch for symptoms like dizziness or fainting. Staying hydrated can help manage blood pressure while on empagliflozin
Does empagliflozin cause weight loss, and should I monitor my weight?
Some people may experience mild weight loss as empagliflozin helps remove excess glucose. Monitoring your weight can help track any unintended changes
Should I stop empagliflozin/Sitagliptin before surgery or a medical procedure?
It’s important to consult your doctor, as empagliflozin may need to be paused before surgery to reduce the risk of DKA. Follow their instructions closely
Can I use empagliflozin/Sitagliptin if I have type 1 diabetes?
Empagliflozin/Sitagliptin is not approved for type 1 diabetes due to a higher risk of diabetic ketoacidosis. It’s only indicated for type 2 diabetes management
How often will my blood glucose and HbA1c levels need to be checked?
Your doctor may check your HbA1c every 3 to 6 months to monitor long-term glucose control. Regular self-monitoring of blood glucose may also be needed, especially if you’re adjusting doses
What to do if you are feeling unwell (vomiting, diarrhea, fever)?
Contact your treating physician immediately and then stop taking Empagliflozin Sitagliptin as per his advise. Once you feel better, start taking Empagliflozin Sitagliptin as per his advise.
What to do if you are having surgery?
Contact your treating physician immediately and then stop taking Empagliflozin Sitagliptin as per his advise.

References
- Adopted from Prescribing information Glyxambi. Available from https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/206073s013lbl.pdf. Cited on 14 Oct 2024
- Summary of Product characteristics. Available from https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/Empagliflozin- Linagliptin-epar-product-information_en.pdf Cited on 14 Oct 2024
- Sick Day Rules for people with type 2 diabetes taking a SGLT-2 Inhibitor https://www.dchft.nhs.uk/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/Sick-Day-Rules-for-people-with-Type-2-Diabetes.pdf Cited on 14 Oct 2024