




Empagliflozin is a medicine belongs to class sodium glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors and used for management of diabetes, heart failure, chronic kidney diseases.
Do not take Empagliflozin, if you are allergic to empagliflozin or any of the other ingredients of this medicine.
Ketoacidosis: If you experience rapid weight loss, feeling sick or being sick, stomach pain, excessive thirst, fast and deep breathing, confusion, unusual sleepiness or tiredness, a sweet smell to your breath, a sweet or metallic taste in your mouth, or a different odour to your urine or sweat, contact a doctor or the nearest hospital straight away.
Talk to your doctor, pharmacist before taking this medicine, and during treatment:
Talk to your doctor immediately if you develop a combination of symptoms of pain, tenderness, redness, or swelling of the genitals or the area between the genitals and the anus with fever or feeling generally unwell. These symptoms could be a sign of a rare but serious or even life-threatening infection, called necrotising fasciitis of the perineum or Fournier´s gangrene which destroys the tissue under the skin. Fournier’s gangrene has to be treated immediately.
Empagliflozin can be used in children aged 10 years and older for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. No data are available in children below 10 years of age. Empagliflozin is not recommended for children and adolescents under 18 years of age for the treatment of heart failure or for the treatment of chronic kidney disease, because it has not been studied in these patients.
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking this medicine. Do not use Empagliflozin if you are pregnant. It is unknown if Empagliflozin is harmful to the unborn child. Do not use Empagliflozin if you are breast-feeding. It is not known if Empagliflozin passes into human breast milk.
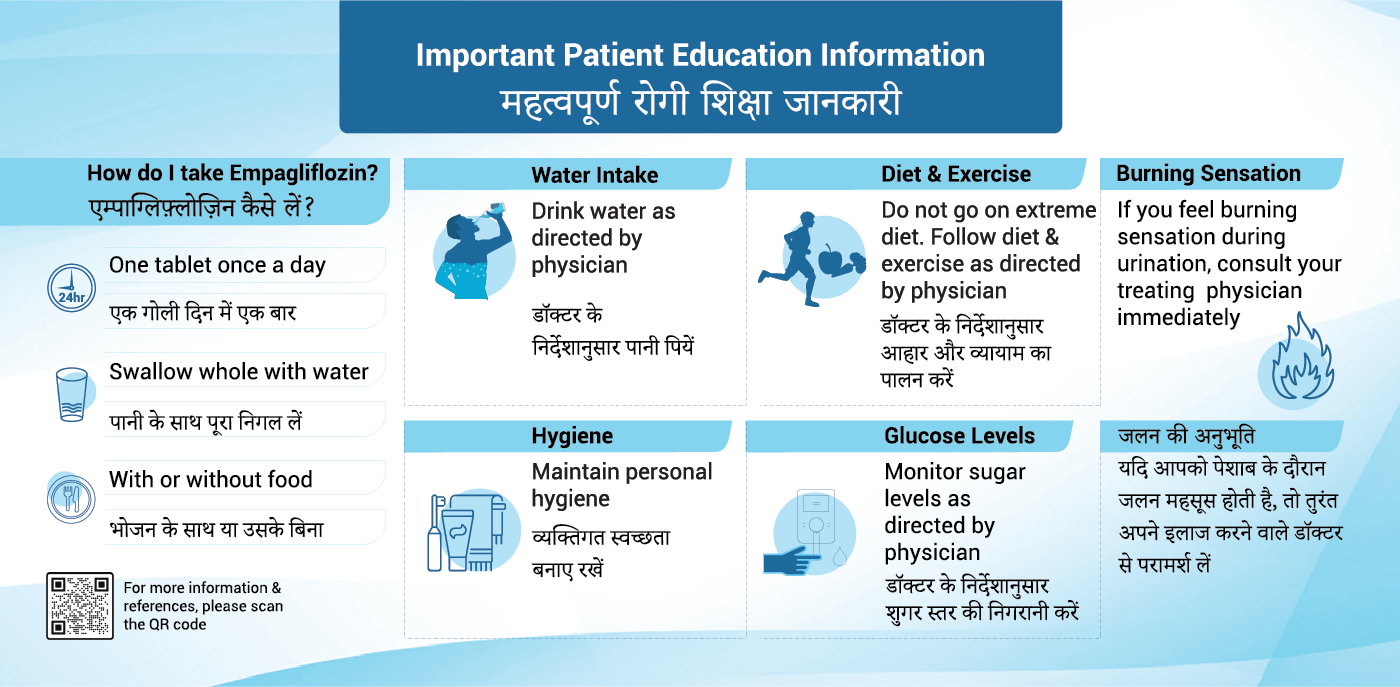
The recommended dose of Empagliflozin is one 10 mg tablet once a day. If you have type 2 diabetes mellitus, your doctor will decide whether to increase your dose to 25 mg once a day, if needed to help to control your blood sugar. Your doctor may limit your dose to 10 mg once a day if you have a kidney problem.
Your doctor will prescribe the strength that is right for you. Do not change your dose unless your doctor has told you to.
What to do if you forget to take a tablet depends on how long it is until your next dose.
If it is 12 hours or more until your next dose, take Empagliflozin as soon as you remember. Then take your next dose at the usual time.
If it is less than 12 hours until your next dose, skip the missed dose. Then take your next dose at the usual time.
Do not take a double dose of Empagliflozin to make up for a forgotten dose.
Do not stop taking Empagliflozin without first consulting your doctor, unless you suspect you have ketoacidosis (see “ketoacidosis” under “warnings and precautions”). If you have type 2 diabetes mellitus, your blood sugar levels may increase when you stop taking Empagliflozin.
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them. Contact a doctor or the nearest hospital straight away if you have any of the following side effects:
Limit alcohol, as it may increase the risk of low blood sugar, especially if you’re also on insulin or other diabetes medications. Reducing high-sugar foods can help manage blood sugar more effectively.
Empagliflozin is not recommended for people with severe kidney impairment (eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m²). If you have kidney disease, your healthcare provider will evaluate your condition to determine if empagliflozin is suitable for you
Symptoms of infection may include painful urination, itching, or unusual discharge. Contact your doctor if you notice any of these signs for prompt treatment
Diuretics, insulin, and sulfonylureas can increase dehydration or hypoglycemia risks when taken with empagliflozin. Inform your doctor of all medications and supplements to avoid potential interactions
Yes, particularly in elderly patients or those on diuretics. Watch for symptoms like dizziness or fainting. Staying hydrated can help manage blood pressure while on empagliflozin
Some people may experience mild weight loss as empagliflozin helps remove excess glucose. Monitoring your weight can help track any unintended changes
It’s important to consult your doctor, as empagliflozin may need to be paused before surgery to reduce the risk of DKA. Follow their instructions closely
Empagliflozin is not approved for type 1 diabetes due to a higher risk of diabetic ketoacidosis. It’s only indicated for type 2 diabetes management
Your doctor may check your HbA1c every 3 to 6 months to monitor long-term glucose control. Regular self-monitoring of blood glucose may also be needed, especially if you’re adjusting doses

Empagliflozin + Linagliptin is a prescription medicine that contains 2 diabetes medicines, empagliflozin and linagliptin. It can be used along with diet and exercise to lower blood sugar in adults with type 2 diabetes, in adults with type 2 diabetes who have known cardiovascular disease when both empagliflozin and linagliptin is appropriate and empagliflozin is needed to reduce the risk of cardiovascular death. Empagliflozin + Linagliptin is not for people with type 1 diabetes.
Do not take Empagliflozin + Linagliptin - if you are allergic to empagliflozin, linagliptin, any other SGLT2 inhibitor (e.g. dapagliflozin, canagliflozin), any other DPP-4 inhibitor (e.g. sitagliptin, vildagliptin), or any of the other ingredients of this medicine.
Contact your doctor if you experience any of the following during treatment with Empagliflozin + Linagliptin :
Talk to your doctor immediately if you develop a combination of symptoms of pain, tenderness, redness, or swelling of the genitals or the area between the genitals and the anus with fever or feeling generally unwell. These symptoms could be a sign of a rare but serious or even life-threatening infection, called necrotising fasciitis of the perineum or Fournier´s gangrene which destroys the tissue under the skin. Fournier’s gangrene has to be treated immediately.
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking this medicine. Do not use Empagliflozin + Linagliptin if you are pregnant. It is unknown if Empagliflozin + Linagliptin is harmful to the unborn child. Do not use Empagliflozin + Linagliptin if you are breast-feeding. It is not known if Empagliflozin/Linagliptin passes into human breast milk.
The usual starting dose is one film-coated tablet of Empagliflozin + Linagliptin 10 mg/5 mg (10 mg empagliflozin and 5 mg linagliptin) once a day. Your doctor will decide whether you need to increase your dose to one film-coated tablet of Empagliflozin + Linagliptin 25 mg/5 mg (25 mg empagliflozin and 5 mg linagliptin) once a day. If you already take 25 mg empagliflozin and 5 mg linagliptin as separate tablets and you switch to Empagliflozin + Linagliptin , you can start directly with Empagliflozin + Linagliptin 25 mg/5 mg.
Talk to your doctor if you have kidney problems. Your doctor may limit your dose or decide to use an alternative medicine. Hepatic impairment Talk to your doctor in case you suffer from severe hepatic impairment. Empagliflozin + Linagliptin is not recommended and your doctor may decide to use an alternative medicine.
empL.Take Empagliflozin + Linagliptin exactly as your doctor tells you to take it.
empL.Take Empagliflozin + Linagliptin 1 time each day in the morning, with or without food.
empL.If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If you do not remember until it is time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and go back to your regular schedule. Do not take two doses of Empagliflozin + Linagliptin at the same time.
empL.If you take too much Empagliflozin + Linagliptin , call your doctor or local poison control center or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
empL.When your body is under some types of stress, such as fever, trauma (such as a car accident), infection, or surgery, the amount of diabetes medicine that you need may change. Tell your doctor right away if you have any of these conditions and follow your doctor’s instructions.
empL.Check your blood sugar as your doctor tells you to.
empL.Stay on your prescribed diet and exercise program while taking Empagliflozin + Linagliptin .
empL.Talk to your doctor about how to prevent, recognize and manage low blood sugar (hypoglycemia), high blood sugar (hyperglycemia), and complications of diabetes.
empL.Your doctor will check your diabetes with regular blood tests, including your blood sugar levels and your hemoglobin A1C.
empL.When taking Empagliflozin + Linagliptin , you may have sugar in your urine, which will show up on a urine test.
What to do if you forget to take a tablet depends on how long it is until your next dose.
If it is 12 hours or more until your next dose, take Empagliflozin + Linagliptin as soon as you remember. Then take your next dose at the usual time.
If it is less than 12 hours until your next dose, skip the missed dose. Then take your next dose at the usual time.
Do not take a double dose of Empagliflozin + Linagliptin to make up for a forgotten dose.
Do not stop taking Empagliflozin + Linagliptin without first consulting your doctor, unless you suspect you have ketoacidosis. If you have type 2 diabetes mellitus, your blood sugar levels may increase when you stop taking Empagliflozin + Linagliptin .
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Contact a doctor or the nearest hospital straight away if you have any of the following side effects:
Diabetic ketoacidosis, seen rarely (may affect up to 1 in 1 000 people)
This may occur regardless of blood glucose level. Your doctor may decide to temporarily or permanently stop your treatment with this medicine.
Contact your doctor immediately if you notice any of the following side effects:
Your doctor will tell you how to treat low blood sugar levels and what to do if you get any of the signs above. If you have symptoms of low blood sugar, eat glucose tablets, a high sugar snack or drink fruit juice. Measure your blood sugar if possible and rest.
An urge to pass urine or more frequent urination may be due to the way this medicine works, but as they can also be signs of urinary tract infection, if you note an increase in such symptoms, you should also contact your doctor.
Seen commonly
Seen uncommonly
empL.Seen rarely
empL.Seen very rarely
empL.If you have kidney disease, your healthcare provider will evaluate your condition to determine if empagliflozin/Linagliptin is suitable for you.
empL.Symptoms of infection may include painful urination, itching, or unusual discharge. Contact your doctor if you notice any of these signs for prompt treatment.
empL.Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using, have recently used or might use any other medicines. In particular, you should tell your doctor if you are using the following medicines:
empL.Yes, particularly in elderly patients or those on diuretics. Watch for symptoms like dizziness or fainting. Staying hydrated can help manage blood pressure while on empagliflozin
empL.Some people may experience mild weight loss as empagliflozin helps remove excess glucose. Monitoring your weight can help track any unintended changes
empL.It’s important to consult your doctor, as empagliflozin may need to be paused before surgery to reduce the risk of DKA. Follow their instructions closely
empL.Empagliflozin/Linagliptin is not approved for type 1 diabetes due to a higher risk of diabetic ketoacidosis. It’s only indicated for type 2 diabetes management
empL.Your doctor may check your HbA1c every 3 to 6 months to monitor long-term glucose control. Regular self-monitoring of blood glucose may also be needed, especially if you’re adjusting doses
empL.Contact your treating physician immediately and then stop taking Empagliflozin Linagliptin as per his advise. Once you feel better, start taking Empagliflozin Linagliptin as per his advise.
empL.Contact your treating physician immediately and then stop taking Empagliflozin Linagliptin as per his advise.
It is a prescription medicine that contains 2 diabetes medicines, empagliflozin and Sitagliptin. It can be used along with diet and exercise to lower blood sugar in adults with type 2 diabetes, in adults with type 2 diabetes who have known cardiovascular disease when empagliflozin, one of the medicines in this FDC, is needed to reduce the risk of cardiovascular death.
Do not take Empagliflozin-sitagliptin- if you are allergic to empagliflozin, sitagliptin, any other SGLT2 inhibitor (e.g. dapagliflozin, canagliflozin), any other DPP-4 inhibitor (e.g. Linagliptin, vildagliptin), or any of the other ingredients of this medicine.
Talk to your doctor, before taking this medicine, and during treatment:
Contact your doctor if you experience any of the following during treatment with Empagliflozin- Sitagliptin:
Talk to your doctor immediately if you develop a combination of symptoms of pain, tenderness, redness, or swelling of the genitals or the area between the genitals and the anus with fever or feeling generally unwell. These symptoms could be a sign of a rare but serious or even life-threatening infection, called necrotizing fasciitis of the perineum or Fournier´s gangrene which destroys the tissue under the skin. Fournier’s gangrene has to be treated immediately.
Foot care: Like for all diabetic patients it is important to check your feet regularly and adhere to any other advice regarding foot care given by your health care professional.
Kidney function: Before you start treatment with Empagliflozin-sitagliptin and regularly during treatment, your doctor will check how well your kidneys are working.
Urine glucose: Because of how this medicine works, your urine will test positive for sugar while you are taking this medicine.
Children and adolescents This medicine is not recommended for children and adolescents under 18 years as sitagliptin is not effective in children and adolescents between the ages of 10 and 17 years. It is not known if this medicine is safe and effective when used in children younger than 10 years
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking this medicine. Do not use Empagliflozin-sitagliptin if you are pregnant. It is unknown if Empagliflozin-sitagliptin is harmful to the unborn child. Do not use Empagliflozin-sitagliptin if you are breast-feeding. It is not known if Empagliflozin/Sitagliptin passes into human breast milk.
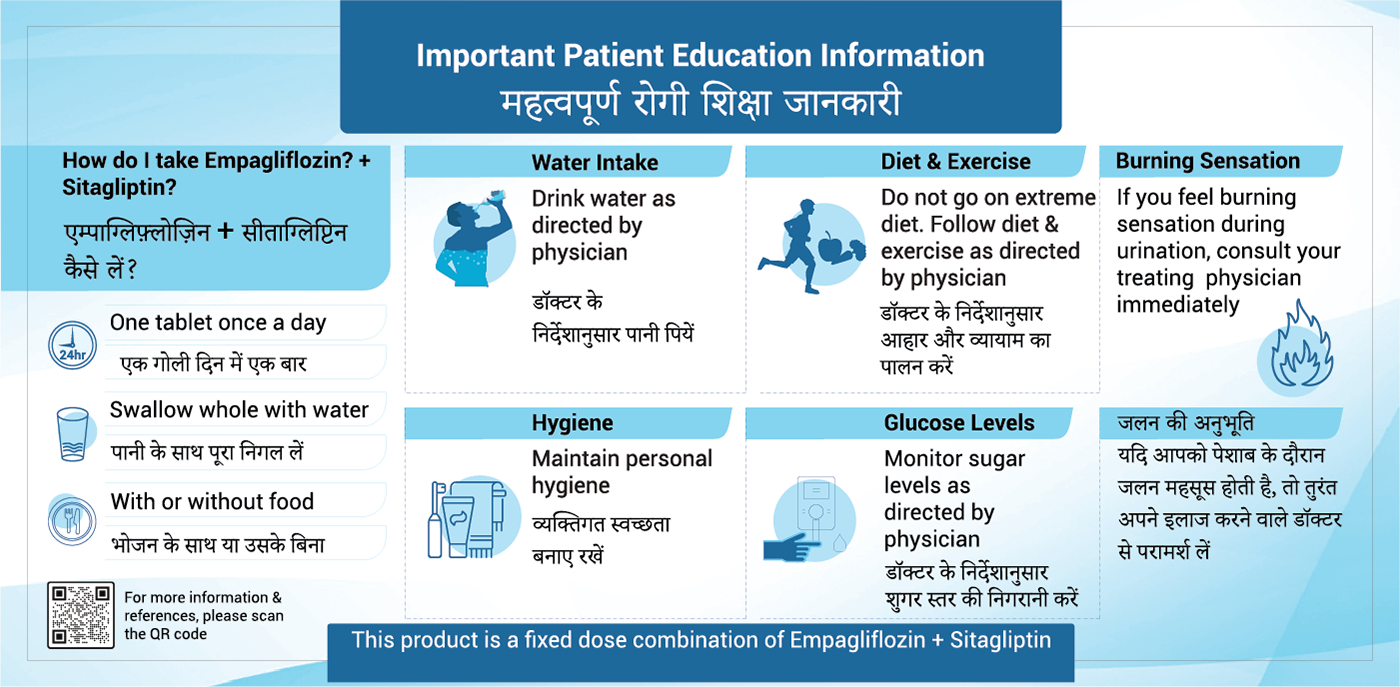
The usual starting dose is one film-coated tablet of Empagliflozin-sitagliptin10 mg/100 mg once a day. Your doctor will decide whether you need to increase your dose to one film-coated tablet of Empagliflozin-sitagliptin 25 mg/100 once a day. If you already take 25 mg empagliflozin and 100 sitagliptin as separate tablets and you switch to the FDC, you can start directly with Empagliflozin-sitagliptin 25 mg/100 mg.
Talk to your doctor if you have kidney problems. Your doctor may limit your dose or decide to use an alternative medicine. Hepatic impairment Talk to your doctor in case you suffer from severe hepatic impairment. Empagliflozin-sitagliptin is not recommended and your doctor may decide to use an alternative medicine.
Take EMPAGLIFLOZIN-SITAGLIPTIN exactly as your doctor tells you to take it.
What to do if you forget to take a tablet depends on how long it is until your next dose.
If it is 12 hours or more until your next dose, take Empagliflozin-sitagliptin as soon as you remember. Then take your next dose at the usual time.
If it is less than 12 hours until your next dose, skip the missed dose. Then take your next dose at the usual time.
Do not take a double dose of Empagliflozin-sitagliptin to make up for a forgotten dose.
Do not stop taking Empagliflozin-sitagliptin without first consulting your doctor, unless you suspect you have ketoacidosis. If you have type 2 diabetes mellitus, your blood sugar levels may increase when you stop taking Empagliflozin- Sitagliptin.
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Contact a doctor or the nearest hospital straight away if you have any of the following side effects
Diabetic ketoacidosis, seen rarely (may affect up to 1 in 1 000 people)
These are the signs of diabetic ketoacidosis (see also section 2, ‘Warnings and precautions’):
This may occur regardless of blood glucose level. Your doctor may decide to temporarily or permanently stop your treatment with this medicine.
Contact your doctor immediately if you notice any of the following side effects:
Allergic reactions, seen uncommonly (may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
This medicine may cause allergic reactions, which may be serious, including hives (urticaria) and swelling of the face, lips, tongue, and throat that may cause difficulty in breathing or swallowing (angioedema).
Inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis), seen uncommonly
This medicine may cause pancreatitis, which usually shows as persistent, severe abdominal (stomach) pain that might reach through to your back, often accompanied by feeling sick or being sick. Your doctor will need to change your treatment.
Low blood sugar (hypoglycaemia), seen commonly (may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
If you take Empagliflozin-sitagliptin with another medicine that can cause low blood sugar, such as a sulphonylurea or insulin, you are at risk of getting too low blood sugar (hypoglycaemia). The signs of too low blood sugar may include:
Your doctor will tell you how to treat low blood sugar levels and what to do if you get any of the signs above. If you have symptoms of low blood sugar, eat glucose tablets, a high sugar snack or drink fruit juice. Measure your blood sugar if possible and rest.
Urinary tract infection, seen commonly
The signs of urinary tract infection are:
An urge to pass urine or more frequent urination may be due to the way this medicine works, but as they can also be signs of urinary tract infection, if you note an increase in such symptoms, you should also contact your doctor.
Loss of body fluid (dehydration), seen uncommonly
The signs of dehydration are not specific, but may include:
Other side effects while taking Empagliflozin- Sitagliptin:
Seen commonly
Seen uncommonly
Seen rarely
Seen very rarely
If you have kidney disease, your healthcare provider will evaluate your condition to determine if empagliflozin/Sitagliptin is suitable for you.
Symptoms of infection may include painful urination, itching, or unusual discharge. Contact your doctor if you notice any of these signs for prompt treatment.
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using, have recently used or might use any other medicines. In particular, you should tell your doctor if you are using the following medicines:
Yes, particularly in elderly patients or those on diuretics. Watch for symptoms like dizziness or fainting. Staying hydrated can help manage blood pressure while on empagliflozin
Some people may experience mild weight loss as empagliflozin helps remove excess glucose. Monitoring your weight can help track any unintended changes
It’s important to consult your doctor, as empagliflozin may need to be paused before surgery to reduce the risk of DKA. Follow their instructions closely
Empagliflozin/Sitagliptin is not approved for type 1 diabetes due to a higher risk of diabetic ketoacidosis. It’s only indicated for type 2 diabetes management
Your doctor may check your HbA1c every 3 to 6 months to monitor long-term glucose control. Regular self-monitoring of blood glucose may also be needed, especially if you’re adjusting doses
Contact your treating physician immediately and then stop taking Empagliflozin Sitagliptin as per his advise. Once you feel better, start taking Empagliflozin Sitagliptin as per his advise.
Contact your treating physician immediately and then stop taking Empagliflozin Sitagliptin as per his advise.

It is a prescription medicine that contains 2 diabetes medicines, empagliflozin and Sitagliptin. It can be used along with diet and exercise to lower blood sugar in adults with type 2 diabetes, in adults with type 2 diabetes who have known cardiovascular disease when empagliflozin, one of the medicines in this FDC, is needed to reduce the risk of cardiovascular death.
Do not take Empagliflozin-sitagliptin- if you are allergic to empagliflozin, sitagliptin, any other SGLT2 inhibitor (e.g. dapagliflozin, canagliflozin), any other DPP-4 inhibitor (e.g. Linagliptin, vildagliptin), or any of the other ingredients of this medicine.
Talk to your doctor, before taking this medicine, and during treatment:
Contact your doctor if you experience any of the following during treatment with Empagliflozin- Sitagliptin:
Talk to your doctor immediately if you develop a combination of symptoms of pain, tenderness, redness, or swelling of the genitals or the area between the genitals and the anus with fever or feeling generally unwell. These symptoms could be a sign of a rare but serious or even life-threatening infection, called necrotizing fasciitis of the perineum or Fournier´s gangrene which destroys the tissue under the skin. Fournier’s gangrene has to be treated immediately.
Foot care: Like for all diabetic patients it is important to check your feet regularly and adhere to any other advice regarding foot care given by your health care professional.
Kidney function: Before you start treatment with Empagliflozin-sitagliptin and regularly during treatment, your doctor will check how well your kidneys are working.
Urine glucose: Because of how this medicine works, your urine will test positive for sugar while you are taking this medicine.
Children and adolescents This medicine is not recommended for children and adolescents under 18 years as sitagliptin is not effective in children and adolescents between the ages of 10 and 17 years. It is not known if this medicine is safe and effective when used in children younger than 10 years
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking this medicine. Do not use Empagliflozin-sitagliptin if you are pregnant. It is unknown if Empagliflozin-sitagliptin is harmful to the unborn child. Do not use Empagliflozin-sitagliptin if you are breast-feeding. It is not known if Empagliflozin/Sitagliptin passes into human breast milk.
The usual starting dose is one film-coated tablet of Empagliflozin-sitagliptin10 mg/100 mg once a day. Your doctor will decide whether you need to increase your dose to one film-coated tablet of Empagliflozin-sitagliptin 25 mg/100 once a day. If you already take 25 mg empagliflozin and 100 sitagliptin as separate tablets and you switch to the FDC, you can start directly with Empagliflozin-sitagliptin 25 mg/100 mg.
Talk to your doctor if you have kidney problems. Your doctor may limit your dose or decide to use an alternative medicine. Hepatic impairment Talk to your doctor in case you suffer from severe hepatic impairment. Empagliflozin-sitagliptin is not recommended and your doctor may decide to use an alternative medicine.
Take EMPAGLIFLOZIN-SITAGLIPTIN exactly as your doctor tells you to take it.
What to do if you forget to take a tablet depends on how long it is until your next dose.
If it is 12 hours or more until your next dose, take Empagliflozin-sitagliptin as soon as you remember. Then take your next dose at the usual time.
If it is less than 12 hours until your next dose, skip the missed dose. Then take your next dose at the usual time.
Do not take a double dose of Empagliflozin-sitagliptin to make up for a forgotten dose.
Do not stop taking Empagliflozin-sitagliptin without first consulting your doctor, unless you suspect you have ketoacidosis. If you have type 2 diabetes mellitus, your blood sugar levels may increase when you stop taking Empagliflozin- Sitagliptin.

Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Contact a doctor or the nearest hospital straight away if you have any of the following side effects
Diabetic ketoacidosis, seen rarely (may affect up to 1 in 1 000 people)
These are the signs of diabetic ketoacidosis (see also section 2, ‘Warnings and precautions’):
This may occur regardless of blood glucose level. Your doctor may decide to temporarily or permanently stop your treatment with this medicine.
Contact your doctor immediately if you notice any of the following side effects:
Allergic reactions, seen uncommonly (may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
This medicine may cause allergic reactions, which may be serious, including hives (urticaria) and swelling of the face, lips, tongue, and throat that may cause difficulty in breathing or swallowing (angioedema).
Inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis), seen uncommonly
This medicine may cause pancreatitis, which usually shows as persistent, severe abdominal (stomach) pain that might reach through to your back, often accompanied by feeling sick or being sick. Your doctor will need to change your treatment.
Low blood sugar (hypoglycaemia), seen commonly (may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
If you take Empagliflozin-sitagliptin with another medicine that can cause low blood sugar, such as a sulphonylurea or insulin, you are at risk of getting too low blood sugar (hypoglycaemia). The signs of too low blood sugar may include:
Your doctor will tell you how to treat low blood sugar levels and what to do if you get any of the signs above. If you have symptoms of low blood sugar, eat glucose tablets, a high sugar snack or drink fruit juice. Measure your blood sugar if possible and rest.
Urinary tract infection, seen commonly
The signs of urinary tract infection are:
An urge to pass urine or more frequent urination may be due to the way this medicine works, but as they can also be signs of urinary tract infection, if you note an increase in such symptoms, you should also contact your doctor.
Loss of body fluid (dehydration), seen uncommonly
The signs of dehydration are not specific, but may include:
Other side effects while taking Empagliflozin- Sitagliptin:
Seen commonly
Seen uncommonly
Seen rarely
Seen very rarely
If you have kidney disease, your healthcare provider will evaluate your condition to determine if empagliflozin/Sitagliptin is suitable for you.
Symptoms of infection may include painful urination, itching, or unusual discharge. Contact your doctor if you notice any of these signs for prompt treatment.
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using, have recently used or might use any other medicines. In particular, you should tell your doctor if you are using the following medicines:
Yes, particularly in elderly patients or those on diuretics. Watch for symptoms like dizziness or fainting. Staying hydrated can help manage blood pressure while on empagliflozin
Some people may experience mild weight loss as empagliflozin helps remove excess glucose. Monitoring your weight can help track any unintended changes
It’s important to consult your doctor, as empagliflozin may need to be paused before surgery to reduce the risk of DKA. Follow their instructions closely
Empagliflozin/Sitagliptin is not approved for type 1 diabetes due to a higher risk of diabetic ketoacidosis. It’s only indicated for type 2 diabetes management
Your doctor may check your HbA1c every 3 to 6 months to monitor long-term glucose control. Regular self-monitoring of blood glucose may also be needed, especially if you’re adjusting doses
Contact your treating physician immediately and then stop taking Empagliflozin Sitagliptin as per his advise. Once you feel better, start taking Empagliflozin Sitagliptin as per his advise.
Contact your treating physician immediately and then stop taking Empagliflozin Sitagliptin as per his advise.

FDC of Empagliflozin Linagliptin Metformin is a prescription medicine that contains 2 diabetes medicines, empagliflozin and linagliptin. It can be used along with diet and exercise to lower blood sugar in adults with type 2 diabetes, in adults with type 2 diabetes who have known cardiovascular disease when empagliflozin, one of the medicines in this FDC, is needed to reduce the risk of cardiovascular death.
Do not take FDC of Empagliflozin Linagliptin Metformin - if you are allergic to empagliflozin, linagliptin, metformin or any of the other ingredients of this medicine.
Talk to your doctor, before taking this medicine, and during treatment:
Contact your doctor if you experience any of the following during treatment with FDC of Empagliflozin Linagliptin Metformin :
Talk to your doctor immediately if you develop a combination of symptoms of pain, tenderness, redness, or swelling of the genitals or the area between the genitals and the anus with fever or feeling generally unwell. These symptoms could be a sign of a rare but serious or even life-threatening infection, called necrotising fasciitis of the perineum or Fournier´s gangrene which destroys the tissue under the skin. Fournier’s gangrene has to be treated immediately.
Foot care: Like for all diabetic patients it is important to check your feet regularly and adhere to any other advice regarding foot care given by your health care professional.
Kidney function: Before you start treatment with FDC of Empagliflozin Linagliptin Metformin and regularly during treatment, your doctor will check how well your kidneys are working.
Urine glucose: Because of how this medicine works, your urine will test positive for sugar while you are taking this medicine.
Children and adolescents This medicine is not recommended for children and adolescents under 18 years as linagliptin is not effective in children and adolescents between the ages of 10 and 17 years. It is not known if this medicine is safe and effective when used in children younger than 10 years
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking this medicine. Do not use FDC of Empagliflozin Linagliptin Metformin if you are pregnant. It is unknown if FDC of Empagliflozin Linagliptin Metformin is harmful to the unborn child. Do not use FDC of Empagliflozin Linagliptin Metformin if you are breast-feeding. It is not known if Empagliflozin/Linagliptin passes into human breast milk.
Take FDC OF EMPAGLIFLOZIN LINAGLIPTIN METFORMIN exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to take it. Take this FDC by mouth 1 time each day with a meal in the morning. Taking this FDC with a meal may lower your chance of having an upset stomach.
Swallow tablets whole. Do not break, cut, crush, dissolve, or chew. If you cannot swallow tablets whole, tell your healthcare provider.
You may see something that looks like the FDC OF EMPAGLIFLOZIN LINAGLIPTIN METFORMIN tablet in your stool (bowel movement). This is not harmful and should not affect the way it works to control your diabetes.
Your healthcare provider will tell you how much FDC OF EMPAGLIFLOZIN LINAGLIPTIN METFORMIN to take and when to take it. Your healthcare provider may change your dose if needed. Your healthcare provider may tell you to take FDC OF EMPAGLIFLOZIN LINAGLIPTIN METFORMIN along with other diabetes medicines.
Talk to your doctor if you have kidney problems. Your doctor may limit your dose or decide to use an alternative medicine. Hepatic impairment Talk to your doctor in case you suffer from severe hepatic impairment. FDC of Empagliflozin Linagliptin Metformin is not recommended and your doctor may decide to use an alternative medicine.
Take FDC OF EMPAGLIFLOZIN LINAGLIPTIN METFORMIN exactly as your doctor tells you to take it.
What to do if you forget to take a tablet depends on how long it is until your next dose.
If it is 12 hours or more until your next dose, take FDC of Empagliflozin Linagliptin Metformin as soon as you remember. Then take your next dose at the usual time.
If it is less than 12 hours until your next dose, skip the missed dose. Then take your next dose at the usual time.
Do not take a double dose of FDC of Empagliflozin Linagliptin Metformin to make up for a forgotten dose.
Do not stop taking FDC of Empagliflozin Linagliptin Metformin without first consulting your doctor, unless you suspect you have ketoacidosis. If you have type 2 diabetes mellitus, your blood sugar levels may increase when you stop taking FDC of Empagliflozin Linagliptin Metformin.
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Contact a doctor or the nearest hospital straight away if you have any of the following side effects:
Lactic acidosis, seen rarely
The signs and symptoms of the condition are
Diabetic ketoacidosis, seen rarely (may affect up to 1 in 1000 people)
These are the signs of diabetic ketoacidosis
This may occur regardless of blood glucose level. Your doctor may decide to temporarily or permanently stop your treatment with this medicine.
Contact your doctor immediately if you notice any of the following side effects:
Allergic reactions, seen uncommonly (may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
This medicine may cause allergic reactions, which may be serious, including hives (urticaria) and swelling of the face, lips, tongue, and throat that may cause difficulty in breathing or swallowing (angioedema).
Inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis), seen uncommonly
This medicine may cause pancreatitis, which usually shows as persistent, severe abdominal (stomach) pain that might reach through to your back, often accompanied by feeling sick or being sick. Your doctor will need to change your treatment.
Low blood sugar (hypoglycaemia), seen commonly (may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
If you take FDC of Empagliflozin Linagliptin Metformin with another medicine that can cause low blood sugar, such as a sulphonylurea or insulin, you are at risk of getting too low blood sugar (hypoglycaemia). The signs of too low blood sugar may include:
Your doctor will tell you how to treat low blood sugar levels and what to do if you get any of the signs above. If you have symptoms of low blood sugar, eat glucose tablets, a high sugar snack or drink fruit juice. Measure your blood sugar if possible and rest.
Urinary tract infection, seen commonly
The signs of urinary tract infection are:
An urge to pass urine or more frequent urination may be due to the way this medicine works, but as they can also be signs of urinary tract infection, if you note an increase in such symptoms, you should also contact your doctor.
Loss of body fluid (dehydration), seen uncommonly
The signs of dehydration are not specific, but may include:
Amputations. SGLT2 inhibitors may increase your risk of lower limb amputations.
You may be at a higher risk of lower limb amputation if you:
Call your healthcare provider right away if you have new pain or tenderness, any sores, ulcers, or infections in your leg or foot. Talk to your healthcare provider about proper foot care.
Low vitamin B (vitamin B deficiency). Using metformin for long periods of time may cause a decrease in the amount of vitamin B in your blood, especially if you have had low vitamin B blood levels before. Your healthcare provider may do blood tests to check your vitamin B levels.
Joint pain. Some people who take linagliptin, one of the medicines in this FDC, may develop joint pain that can be severe. Call your healthcare provider if you have severe joint pain.
Other side effects while taking FDC of Empagliflozin Linagliptin Metformin :
Seen commonly
Seen uncommonly
Seen rarely
Seen very rarely
If you have kidney disease, your healthcare provider will evaluate your condition to determine if empagliflozin/Linagliptin/metformin is suitable for you.
Symptoms of infection may include painful urination, itching, or unusual discharge. Contact your doctor if you notice any of these signs for prompt treatment.
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using, have recently used or might use any other medicines. In particular, you should tell your doctor if you are using the following medicines:
Yes, particularly in elderly patients or those on diuretics. Watch for symptoms like dizziness or fainting. Staying hydrated can help manage blood pressure while on empagliflozin
Some people may experience mild weight loss as empagliflozin helps remove excess glucose. Monitoring your weight can help track any unintended changes
It’s important to consult your doctor, as empagliflozin may need to be paused before surgery to reduce the risk of DKA. Follow their instructions closely
Empagliflozin/Linagliptin is not approved for type 1 diabetes due to a higher risk of diabetic ketoacidosis. It’s only indicated for type 2 diabetes management
Your doctor may check your HbA1c every 3 to 6 months to monitor long-term glucose control. Regular self-monitoring of blood glucose may also be needed, especially if you’re adjusting doses
Contact your treating physician immediately and then stop taking Empagliflozin Linagliptin as per his advise. Once you feel better, start taking Empagliflozin Linagliptin as per his advise.
Contact your treating physician immediately and then stop taking Empagliflozin Linagliptin as per his advise.
FDC of empagliflozin metformin is a diabetes medicine that contains two active substances called empagliflozin and metformin.
FDC of empagliflozin metformin is added to diet and exercise to treat type 2 diabetes in adult patients (aged 18 years and older) whose diabetes cannot be controlled by adding metformin alone or metformin with other medicines for diabetes.
FDC of empagliflozin metformin can also be combined with other medicines. These may be medicines taken by mouth or insulin given by injection.
In addition, FDC of empagliflozin metformin can be used as an alternative to taking both empagliflozin and metformin as single tablets. To avoid overdose, do not continue taking empagliflozin and metformin tablets separately, if you are taking this medicine.
It is important that you continue with your diet and exercise plan as told by your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
Type 2 diabetes is a disease that comes from both your genes and your lifestyle. If you have type 2 diabetes, your pancreas does not make enough insulin to control the level of glucose in your blood, and your body is unable to use its own insulin effectively. This results in high levels of glucose in your blood which can lead to medical problems like heart disease, kidney disease, blindness, and poor circulation in your limbs.
What you need to know before you take FDC of empagliflozin metformin Do not take FDC of empagliflozin metformin:
Talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse before taking this medicine, and during treatment:
Due to the metformin component, FDC of empagliflozin metformin may cause a very rare, but very serious complication called lactic acidosis, particularly if your kidneys are not working properly. The risk of developing lactic acidosis is also increased with uncontrolled diabetes, prolonged fasting or alcohol intake, body fluid deficit (dehydration) due to severe diarrhoea or vomiting, liver problems and any medical conditions in which a region of the body is deprived with a lack of oxygen supply (such as acute severe heart diseases).
It is important to you to comply with your medication intake, dietary instructions and regular exercise program because this can reduce the risk of lactic acidosis.
The onset of lactic acidosis can be subtle and the symptoms can be non-specific such as vomiting, bellyache (abdominal pain) with muscle cramps, a general feeling of not being well with severe tiredness, and difficulty in breathing. Further symptoms are reduced body temperature and heart beat. If you experience some of these symptoms, you should seek immediately medical attention, as lactic acidosis may lead to coma. Stop taking FDC of empagliflozin metformin immediately and contact a doctor or the nearest hospital straight away.
Your kidneys will be tested by a blood test before you start taking and while you are taking this medicine.
Because of how this medicine works, your urine will test positive for sugar while you are taking this medicine.
This medicine is not recommended for use in children and adolescents under 18 years, because it has not been studied in these patients.
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines.
It is important to tell your doctor if you are taking:
There is an increased risk of lactic acidosis following excessive alcohol consumption (particularly in the case of fasting, malnutrition, or liver disease). Therefore, avoid consumption of alcohol and medicines containing alcohol when taking FDC of empagliflozin metformin (see section 4, ‘Possible side effects’).
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking this medicine.
Do not take FDC of empagliflozin metformin if you are pregnant. It is unknown if this medicine is harmful to the unborn child.
Metformin passes into human milk in small amounts. It is not known whether empagliflozin passes into human breast milk. Do not take FDC of empagliflozin metformin if you are breast-feeding.
FDC of empagliflozin metformin has minor influence on the ability to drive and use machines.
Taking this medicine in combination with medicines called sulphonylureas or with insulin can cause blood sugar levels to drop too low (hypoglycaemia), which may cause symptoms such as shaking, sweating and change in vision, and may affect your ability to drive and use machines. Do not drive or use any tools or machines if you feel dizzy while taking FDC of empagliflozin metformin.
Always take this medicine exactly as your doctor has told you. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure.
The dose of FDC of empagliflozin metformin varies depending on your condition and the doses of diabetes medicines you currently take. Your doctor will adjust your dose as necessary and tell you exactly which strength of the medicine to take.
Your doctor may prescribe FDC of empagliflozin metformin together with another diabetes medicine. Remember to take all medicines as directed by your doctor to achieve the best results for your health. Your doctor may need to adjust your doses to control your blood sugar.
Diet and exercise can help your body use its blood sugar better. It is important to stay on the diet and exercise program recommended by your doctor while taking FDC of empagliflozin metformin.
If you take more FDC of empagliflozin metformin tablets than you should have, you may experience lactic acidosis. Symptoms of lactic acidosis are non-specific such as feeling or being very sick, vomiting, stomach ache with muscle cramps, a general feeling of not being well with severe tiredness, and difficulty in breathing. Further symptoms are reduced body temperature and heart beat. If this happens to you, you may need immediate hospital treatment, as lactic acidosis can lead to coma. Stop taking this medicine immediately and contact a doctor or the nearest hospital straight away. Take the medicine pack with you.
If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If you do not remember until it is time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and go back to your regular schedule. Do not take a double dose of this medicine.
Do not stop taking FDC of empagliflozin metformin without first consulting your doctor. Your blood sugar levels may increase when you stop taking FDC of empagliflozin metformin.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Lactic acidosis. Metformin, one of the active substances in this medicine, can cause a very rare (may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people) but serious side effect called ‘lactic acidosis’. This is a build-up of lactic acid in the blood that can cause death. Lactic acidosis is a medical emergency and must be treated in hospital. It particularly affects patients whose kidneys are not working properly.
Signs of ‘lactic acidosis’ are:
If this happens to you, you may need immediate hospital treatment, as lactic acidosis may lead to coma. Stop taking this medicine immediately and contact a doctor or the nearest hospital straight away. Take the medicine pack with you.
Contact a doctor or the nearest hospital straight away if you have any of the following side effects:
Diabetic ketoacidosis, seen rarely (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people)
These are the signs of diabetic ketoacidosis (see also section 2, ‘Warnings and precautions’):
This may occur regardless of blood glucose level. Your doctor may decide to temporarily or permanently stop your treatment with FDC of empagliflozin metformin.
Contact your doctor as soon as possible if you notice the following side effects:
Low blood sugar (hypoglycaemia), seen very commonly (may affect more than 1 in 10 people) If you take FDC of empagliflozin metformin with another medicine that can cause low blood sugar, such as a sulfonylurea or insulin, your risk of getting low blood sugar is increased. The signs of low blood sugar may include:
Your doctor will tell you how to treat low blood sugar levels and what to do if you get any of the signs above. If you have symptoms of low blood sugar, eat glucose tablets, a high sugar snack or drink fruit juice. Measure your blood sugar if possible and rest.
Urinary tract infection, seen commonly (may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
The signs of urinary tract infection are:
An urge to pass urine or more frequent urination may be due to the way FDC of empagliflozin metformin works, but as they can also be signs of urinary tract infection. If you note an increase in such symptoms, you should also contact your doctor.
Dehydration, seen uncommonly (may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
The signs of dehydration are not specific, but may include:
Other side effects while taking FDC of empagliflozin metformin:
Very common
Common
Uncommon
Very rare
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. By reporting side effects you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the blister and the carton after ‘EXP’. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
This medicine does not require any special storage conditions.
Do not use this medicine if you notice that the packaging is damaged or shows signs of tampering.
Do not throw away any medicines via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines you no longer use. These measures will help protect the environment.
If you have kidney disease, your healthcare provider will evaluate your condition to determine if empagliflozin/Sitagliptin is suitable for you.
Symptoms of infection may include painful urination, itching, or unusual discharge. Contact your doctor if you notice any of these signs for prompt treatment.
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using, have recently used or might use any other medicines. In particular, you should tell your doctor if you are using the following medicines:
Yes, particularly in elderly patients or those on diuretics. Watch for symptoms like dizziness or fainting. Staying hydrated can help manage blood pressure while on empagliflozin
Some people may experience mild weight loss as empagliflozin helps remove excess glucose. Monitoring your weight can help track any unintended changes
It’s important to consult your doctor, as empagliflozin may need to be paused before surgery to reduce the risk of DKA. Follow their instructions closely
Empagliflozin/Sitagliptin is not approved for type 1 diabetes due to a higher risk of diabetic ketoacidosis. It’s only indicated for type 2 diabetes management
Your doctor may check your HbA1c every 3 to 6 months to monitor long-term glucose control. Regular self-monitoring of blood glucose may also be needed, especially if you’re adjusting doses
Contact your treating physician immediately and then stop taking Empagliflozin Sitagliptin as per his advise. Once you feel better, start taking Empagliflozin Sitagliptin as per his advise.
Contact your treating physician immediately and then stop taking Empagliflozin metformin as per his advise.